Click on a thumbnail graphic to view a gallery of drought data from the US Drought Monitor website.


Click the link to go to the US Drought Monitor website. Here’s an excerpt:
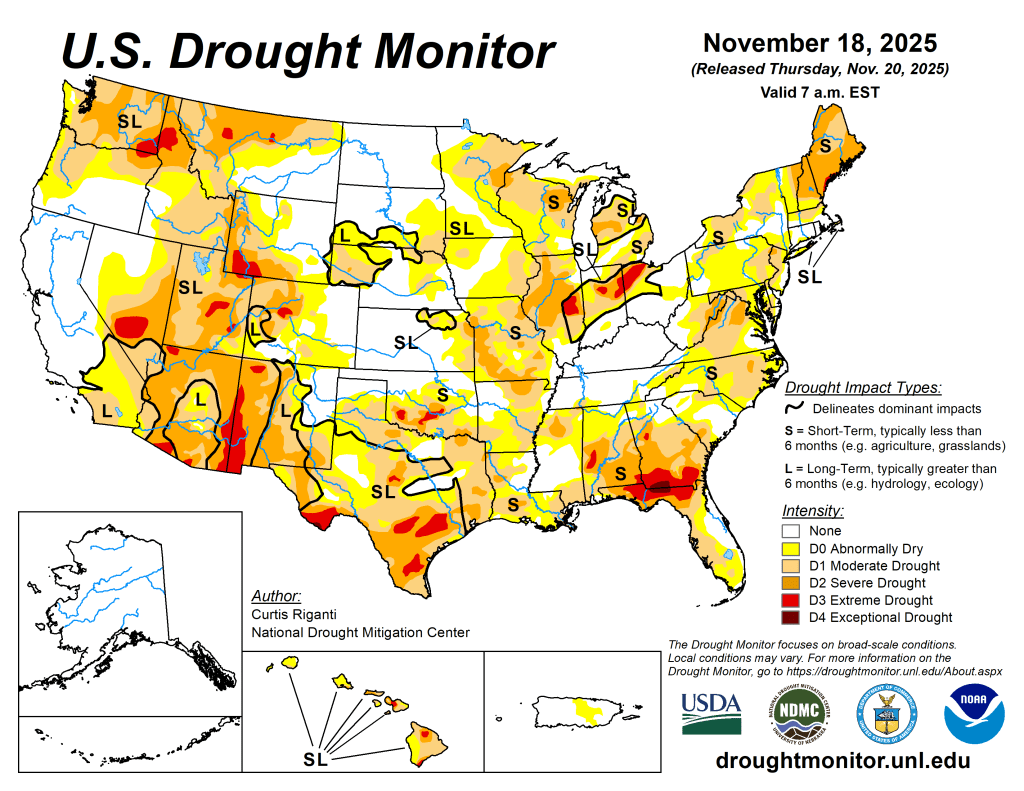
This Week’s Drought Summary
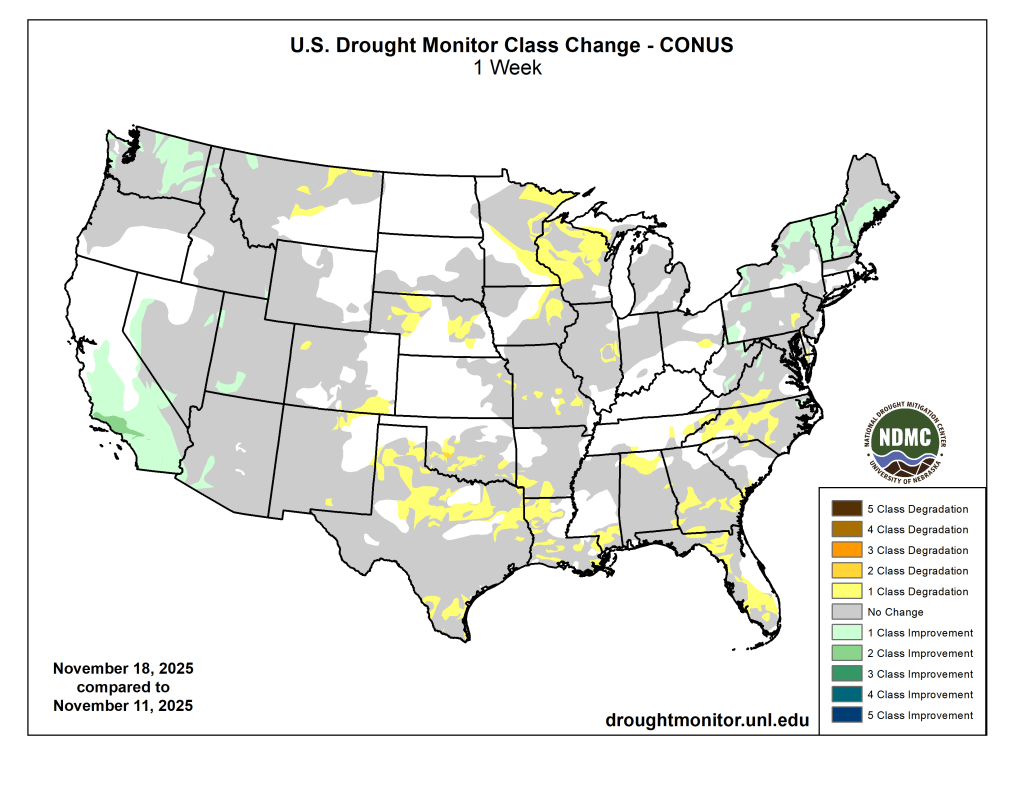
Dry weather covered most of the central and eastern U.S. this week, with a few localized areas of heavier precipitation falling in the Northeast and parts of eastern South Dakota. In the West, heavy rain and snow was widespread, especially in parts of southern Nevada, southern and coastal California, the Sierra Nevada, the Pacific Northwest and northwest Montana. Temperatures west of the Mississippi River were mostly warmer than normal, especially in Montana and Wyoming, where temperatures of 12 or more degrees above normal were common. East of the Mississippi River, near- or below-normal temperatures were widespread, especially in southern Georgia and Florida, where temperatures were 6-12 degrees colder than normal. Given the wetter weather recently, improvements continued in parts of the Northeast, where streamflow and soil moisture continued to recover and precipitation deficits lessened. Improvements were also widespread in California and Washington, where recent precipitation has cut into or erased precipitation deficits and boosted soil moisture and streamflow. Degradations were common in Oklahoma, Texas, Louisiana, Florida, Georgia and North Carolina, where short-term precipitation deficits grew. Widespread degradation also occurred in parts of Nebraska, central and northeast Montana and the western Great Lakes area, as primarily short-term dryness intensified in each of these areas. Recent pockets of drier- or wetter-than-normal weather led to a few small changes in areas of abnormal dryness in Puerto Rico. Wetter weather in the windward sides of Hawaii led to local improvements on Oahu, Maui and the Big Island, where streamflows have responded well to increased precipitation…
High Plains
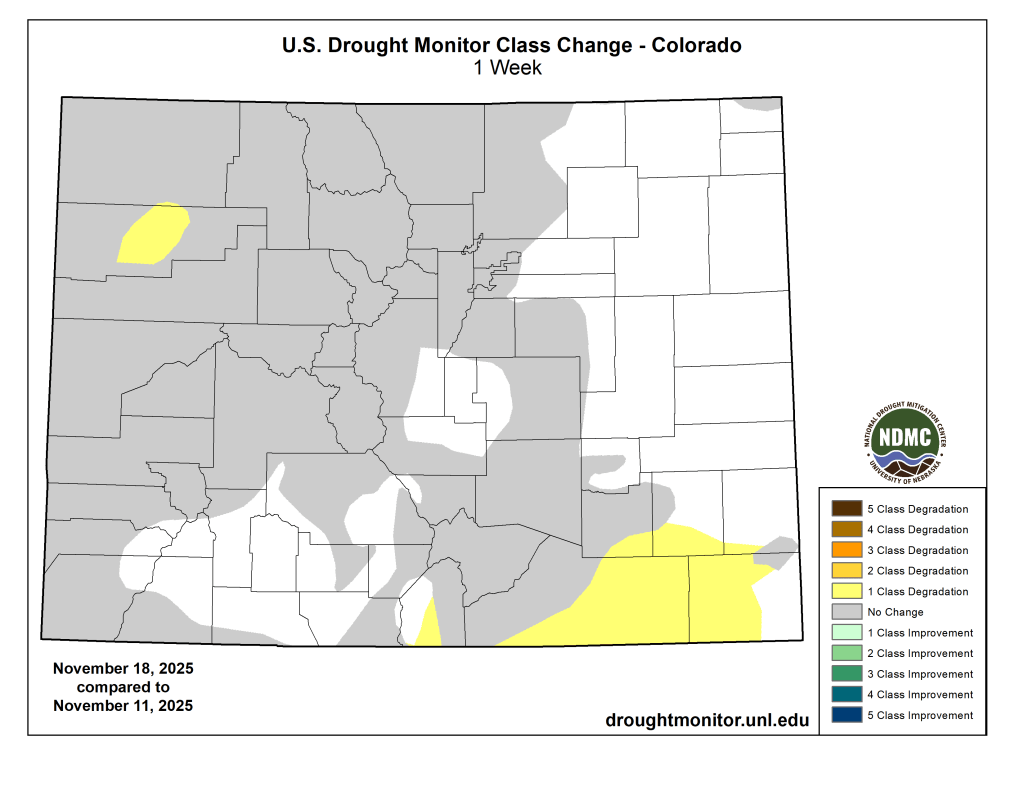
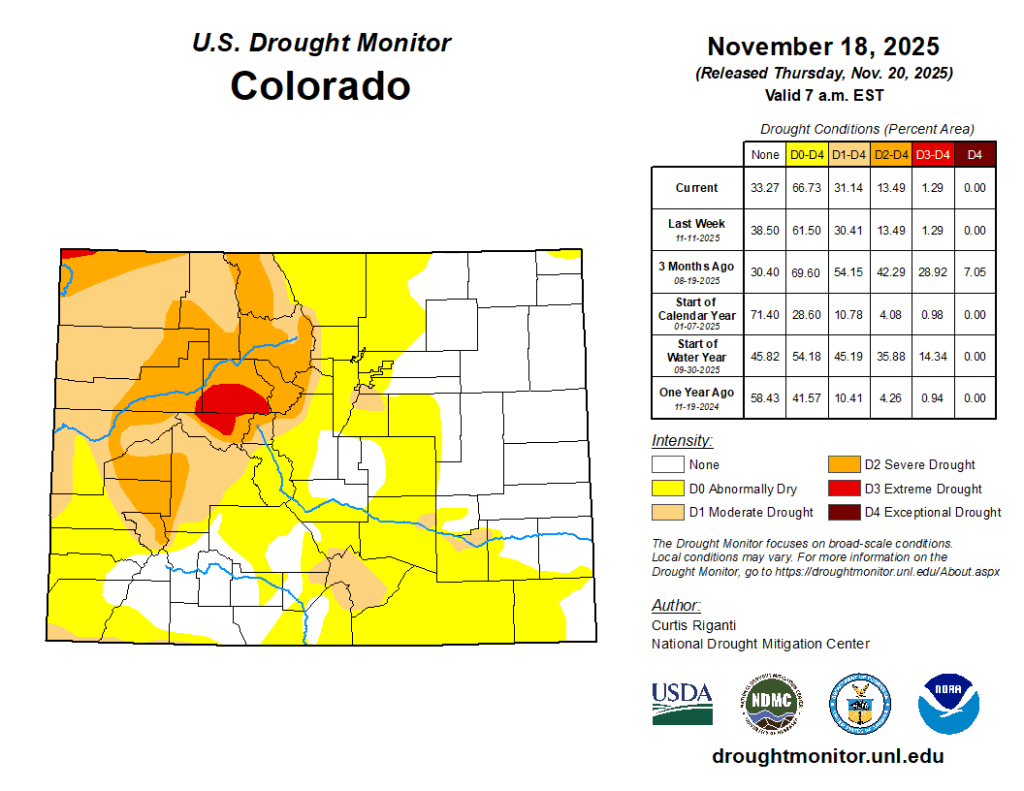
Primarily dry and warmer-than-normal weather occurred in the High Plains region this week, with the exceptions of east-central South Dakota and some high-elevation areas of Colorado and Wyoming. Temperatures in Wyoming and parts of eastern Colorado were 12 or more degrees above normal this week, while eastern parts of the Dakotas, Nebraska and Kansas were mostly 3-9 degrees warmer than normal. Short-term precipitation deficits and decreasing soil moisture in some areas led to expansions and development of abnormal dryness and moderate drought in parts of eastern and central Nebraska. In western Nebraska, abnormal dryness and moderate drought expanded under similar conditions, while severe drought also developed where more substantial longer-term precipitation deficits were taking place. In and near the Kansas City area, moderate and severe drought locally expanded where soil moisture levels decreased and short-term precipitation shortfalls grew. Abnormal dryness expanded across the southeast Colorado plains where short-term precipitation deficits grew, while moderate drought filled in in northwest Colorado where short-term dryness aligned with long-term precipitation deficits…
West
Widespread heavy precipitation fell this week in California, southern Nevada, the Pacific Northwest and northern Idaho and northwest Montana. Locally over 5 inches of precipitation fell in northwest Washington, spots in northwest Montana and northern Idaho, and across scattered parts of California, especially in some coastal regions and the Sierra Nevada. Soil moisture levels increased across California amid the heavy precipitation. Precipitation deficits lessened in many areas or were entirely removed, leading to widespread 1-category improvements in California and localized 2-category improvements near Los Angeles. As the impact of this precipitation on the water cycle in California and Nevada is evaluated in the coming weeks, further improvements may occur. Conditions also improved after recent precipitation cut into precipitation deficits and locally improved soil moisture, groundwater and streamflow in northwest Washington, central and eastern Washington, northern Idaho and northwest Montana, southwest Arizona, and southwest Utah and along a portion of the Utah-Nevada border. Despite the widespread precipitation, weekly temperature anomalies were warm across the entire West this week. Compared to normal, Montana and Idaho were generally the warmest, with parts of Montana and southern Idaho finishing the week 12 degrees or more warmer than normal. In the plains of central and northeast Montana, moderate and severe drought and abnormal dryness quickly worsened amid warmer-than-normal temperatures and drier weather. In these areas, streamflow locally decreased amid growing soil moisture and short-term precipitation deficits…
South
Dry weather occurred across nearly the entire South region this week, which led to widespread degradations in conditions in some states. Warmer-than-normal temperatures occurred in parts of Texas and Oklahoma and some locales in Arkansas, while near- or below-normal temperatures were more common elsewhere. In the Texas Panhandle and southwest parts of the Lone Star State, temperatures of at least 9 degrees above normal were common. South of Oklahoma City, extreme drought developed where ponds dried up amid large short-term precipitation deficits and above-normal evaporative demand. Degradations occurred across large parts of southern Oklahoma where short-term precipitation deficits continued amid above-normal temperatures. A mix of short- and long-term precipitation deficits and warm temperatures led to degradations in southern Texas, while conditions also degraded in parts of north Texas and the Texas Panhandle during recent dry and warm weather. Short-term precipitation deficits also grew in much of northeast Texas, Louisiana, southwest Arkansas and southern Mississippi, leading to degrading conditions. Streamflow and soil moisture levels also were low in some areas that worsened this week…
Looking Ahead
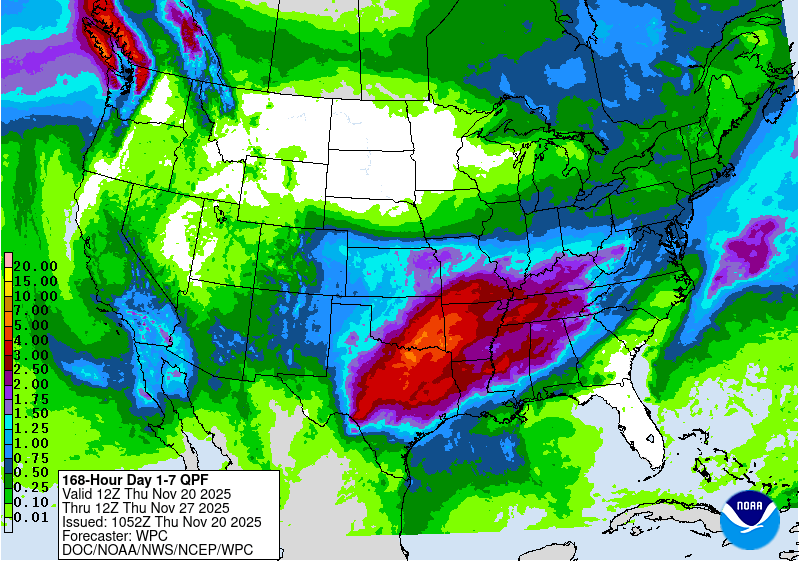
From the evening of Nov. 19 through Nov. 24, the National Weather Service Weather (NWS) Prediction Center is forecasting a large area to receive near or over 1 inch of precipitation from southern Ohio eastward to northeast Colorado and south to northwest Louisiana and much of Oklahoma and Texas (excluding the southwest). Precipitation amounts of at least 0.75 inches are also forecast in parts of southern California, southern Arizona and southeast two-thirds of New Mexico. Heavy precipitation, locally exceeding 3 inches, is forecast in parts of western Washington. Mostly dry weather is forecast across the northern Great Plains and from the Upper Midwest eastward to most of New York and northern New England. Dry weather is also likely to continue in much of the Southeast, especially in drought-stricken areas of southeast Louisiana, southern Georgia and Florida.
For Nov. 25-29, the NWS Climate Prediction Center forecast favors above-normal precipitation across parts of the northern, central and eastern U.S. The highest confidence areas for above-normal precipitation include the northern Great Plains and the Southeast. Drier-than-normal weather is favored in the Southwest U.S., especially in coastal California, southeast Arizona, southern New Mexico and southwest Texas. The forecast favors colder-than-normal temperatures from northern Washington east to Lake Superior and southward through the central Great Plains. In the West, warmer-than-normal temperatures are likelier from central Oregon southward along the Pacific Coast and eastward to near the Continental Divide. The forecast favors warmer-than-normal temperatures in areas from the Gulf Coast to the Mid-Atlantic, with the highest confidence for warmth centered over the Southeast.
In Hawaii, above-normal temperatures and precipitation are favored across the state. In Alaska, the forecast favors warmer-than-normal temperatures in central and western parts of the state, while southeast Alaska is more likely to be colder than normal. Above-normal precipitation is favored for the southwest part of Alaska, while the forecast leans towards below-normal precipitation in northern and southeast Alaska.