Click the link to read the article on the AZCentral.com website (Brandon Loomis). Here’s an excerpt:
December 15, 2025
Key Points
- Seven states and 30 tribes that depend on the Colorado River are looking for ways to share a shrinking resource, but environmental groups fear little will be left for the river itself.
- A wetlands at the end of the river and a fishery at its midpoint show what can happen when water is managed to preserve nature’s needs.
- Growing demand on the river and competing interests, including electric power providers, could force negotiators for the states to confront difficult decisions.
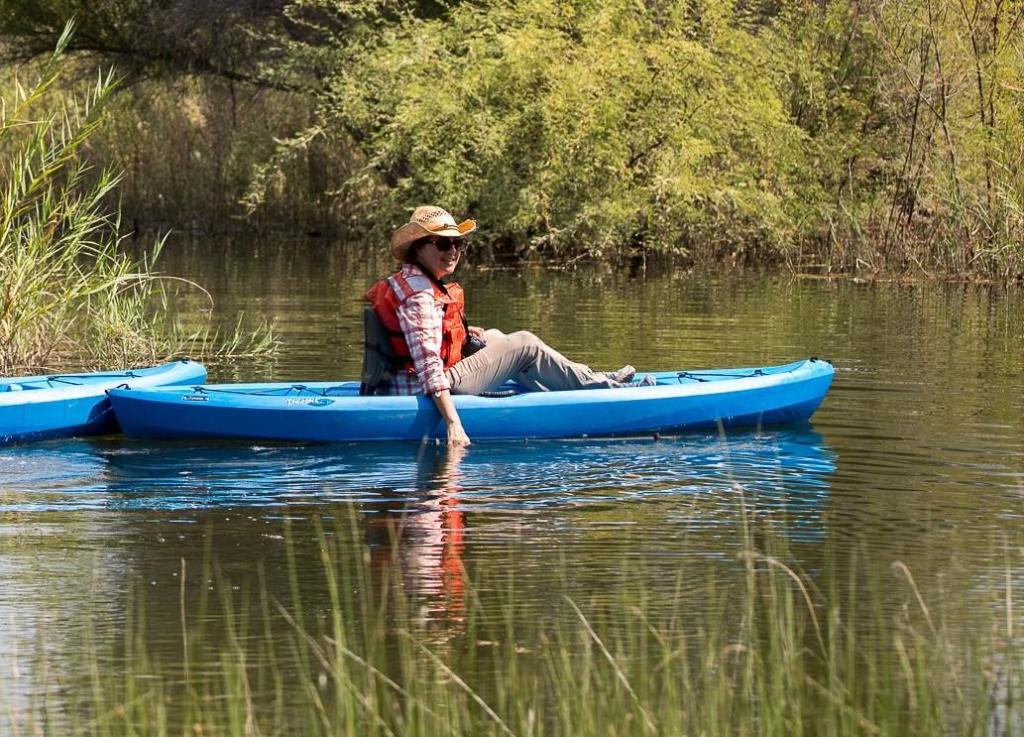
CIÉNEGA DE SANTA CLARA, Mexico — The rusty observation tower at the edge of this wastewater-fed marsh offers an osprey-eye view of two possible futures for the parched and overworked Colorado River. To one side, the marsh spreads across more than 20 square miles of pools and islands choked with cattails and phragmites, convoys of pelicans descending and splashing down for a rest on their journey south from the Great Salt Lake or other western waters. Dragonflies hover below, while a fish hawk circles above, scanning the open water between the reeds. This is a vision of a future in which partners across the Western United States and Mexico save enough water that they can spare some for nature, even if it means irrigating it with the salty dregs. On the tower’s other side, boundless flats of sand and cracked mud spread to the horizon across what was, prior to the river’s damming a century ago, one of Earth’s great green estuaries.

Jennifer Pitt leaned against a rail atop the tower and scanned that dusty horizon. A century ago, she said, the river had meandered so widely and soaked so much verdant ground there that the naturalist Aldo Leopold had written in “A Sand County Almanac” that “the river was nowhere and everywhere,” unable to “decide which of a hundred green lagoons offered the most pleasant and least speedy path to the Gulf (of California).”
Now the Grand River’s delta supports just a handful of green lagoons, all fed either by wastewater or by targeted environmental irrigation. Pitt leads the Audubon Society’s Colorado River program. She has toiled for decades alongside American and Mexican conservationists to rebuild slivers of living delta from what’s left of the water after dams, farm ditches and growing cities divert most of the great river along its 1,450-mile route from the Rocky Mountains toward its dry mouth on the Sea of Cortez near here. A century ago, the river would have wandered a soaked delta teeming with birds, jaguars and legendary biodiversity. Now, a wastewater marsh must do the ecological heavy lifting.

“If we can’t prioritize taking care of a place like this, I fear for our ability to take care of ourselves,” Pitt said.
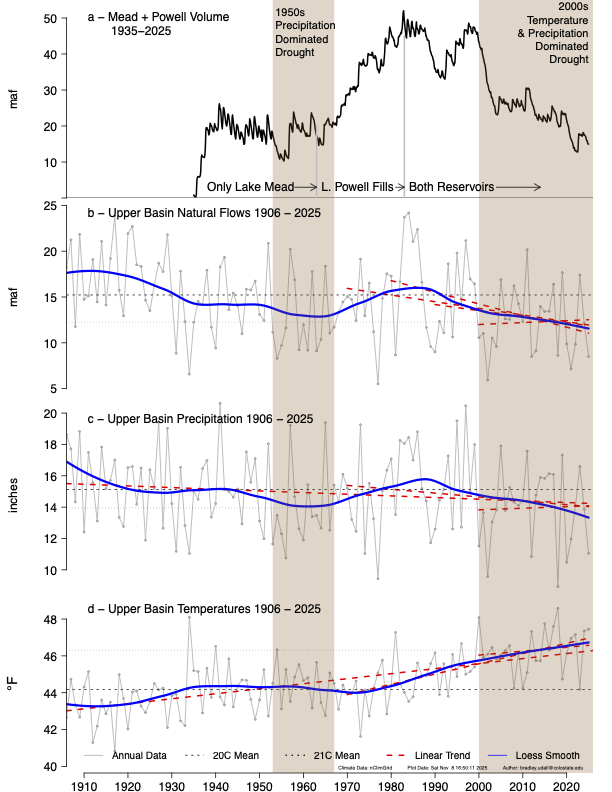
The next few months will be a turning point in efforts to preserve a measure of nature here and across the river’s length, as the seven U.S. states that split the bulk of the water struggle to reach a new deal among themselves that could also determine how much water is available to nurse a remnant of the river’s own environment. Federal officials have said Interior Secretary Doug Burgum is prepared to impose his own cuts if the states can’t reach their own deal, and have said they need a negotiated plan by late winter to avoid that outcome. More than two decades of “megadrought,” unprecedented in U.S. history, have left little wiggle room for year-to-year operations. Reservoirs that were near their 58.48 million-acre-foot capacity in 2000 began the 2026 water year on Oct. 1, with just 21.8 million acre-feet behind the dams. Each acre-foot contains about 326,000 gallons and is roughly enough to support three households for a year, though the bulk of the water flows to the region’s farms.

